Parvo-Corona IC
Rapid test for the detection of Parvovirus and Canine Coronavirus antigen.
Parvo / Corona IC is an immunochromatographic test for the detection of Canine Parvovirus (CPV) and Canine Coronavirus (CCoV) antigens in canine faeces samples.
Corona 95.2%
Corona 99.2%
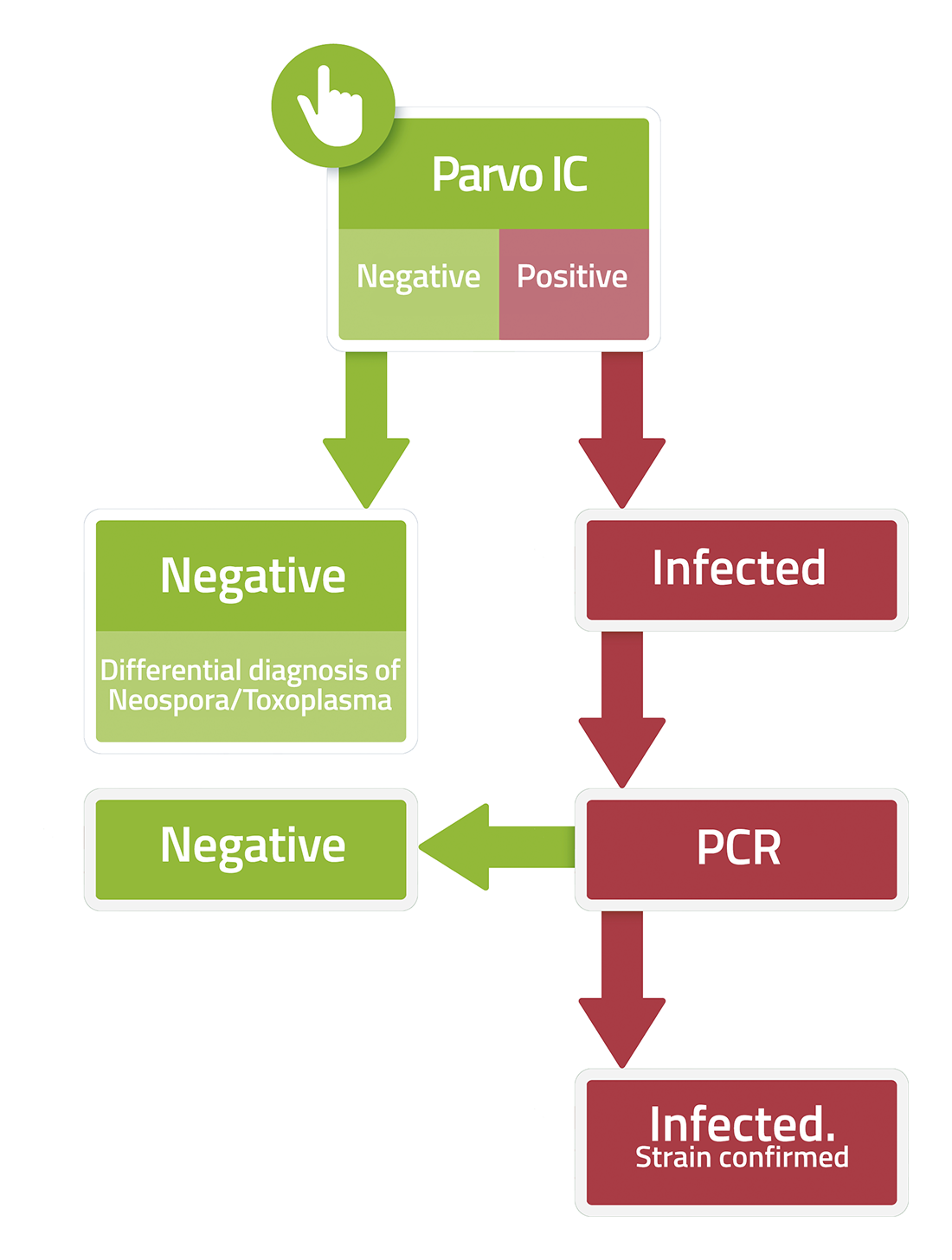
PARVO
Parvo is a highly contagious viral disease that can be potentially fatal, especially in unvaccinated puppies.
The responsible virus is classified as Canine Parvovirus Type 2 (CPV 2), to distinguish it from another Parvovirus (CPV 1) found in dog feces, without pathological significance. It is a very resistant virus in the environment (it can also withstand up to 1 year) and to the action of detergents and disinfectants.
The virus is excreted in the faeces and multiplies in the digestive tract and bone marrow. Penetrated into the body orally, after an incubation period of 3-8 days, the virus initially replicates in the oropharyngeal lymphatic tissues, from which it spreads haematogenously to all tissues. Subsequently, the virus localizes to the lymphohematous tissues of the bone marrow and to the lymphoid tissues of the jejunum and ileum, where it causes respectively neutropenia, lymphopenia, destruction of the intestinal villi with necrosis of the epithelium and hemorrhagic diarrhoea. As a result of immunosuppression, infected animals have frequent secondary bacterial infections (from Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Campylobacter and clostridia) which aggravate the pathogenetic picture. From the 3rd day post-infection the animal becomes a virus eliminator.
Infection can occur by direct contact with the faeces of infected dogs or indirectly through exposure to the environment or to contaminated objects, such as litter boxes or bowls.
Parvoviral infection can affect dogs of any age, although most cases occur in young puppies between the ages of 6 weeks and 6 months. Unvaccinated or partially vaccinated animals have a considerably higher risk of developing parvo.
Some breeds are described as predisposed to canine parvovirus infection, such as Dobermann Pinscher, Rottweiler, English Springer Spaniel, German Shepherd, American Pit Bull Terrier and Dachshund. These breeds, once infected, also tend to develop more severe symptoms.
Toy Poodles and Cocker Spaniels appear to have a reduced risk of canine parvovirus infection. Puppies whose mothers have been regularly vaccinated are also affected less frequently and less severely by parvo. This is because vaccination from the mother increases the levels of circulating maternal antibodies in young puppies. The spread of canine parvo is worldwide. The first episodes of canine parvovirus sustained by CPV were observed in 1978 in America, the disease spread rapidly throughout the world, affecting wild canids and domestic dogs, soon becoming an endemic disease.
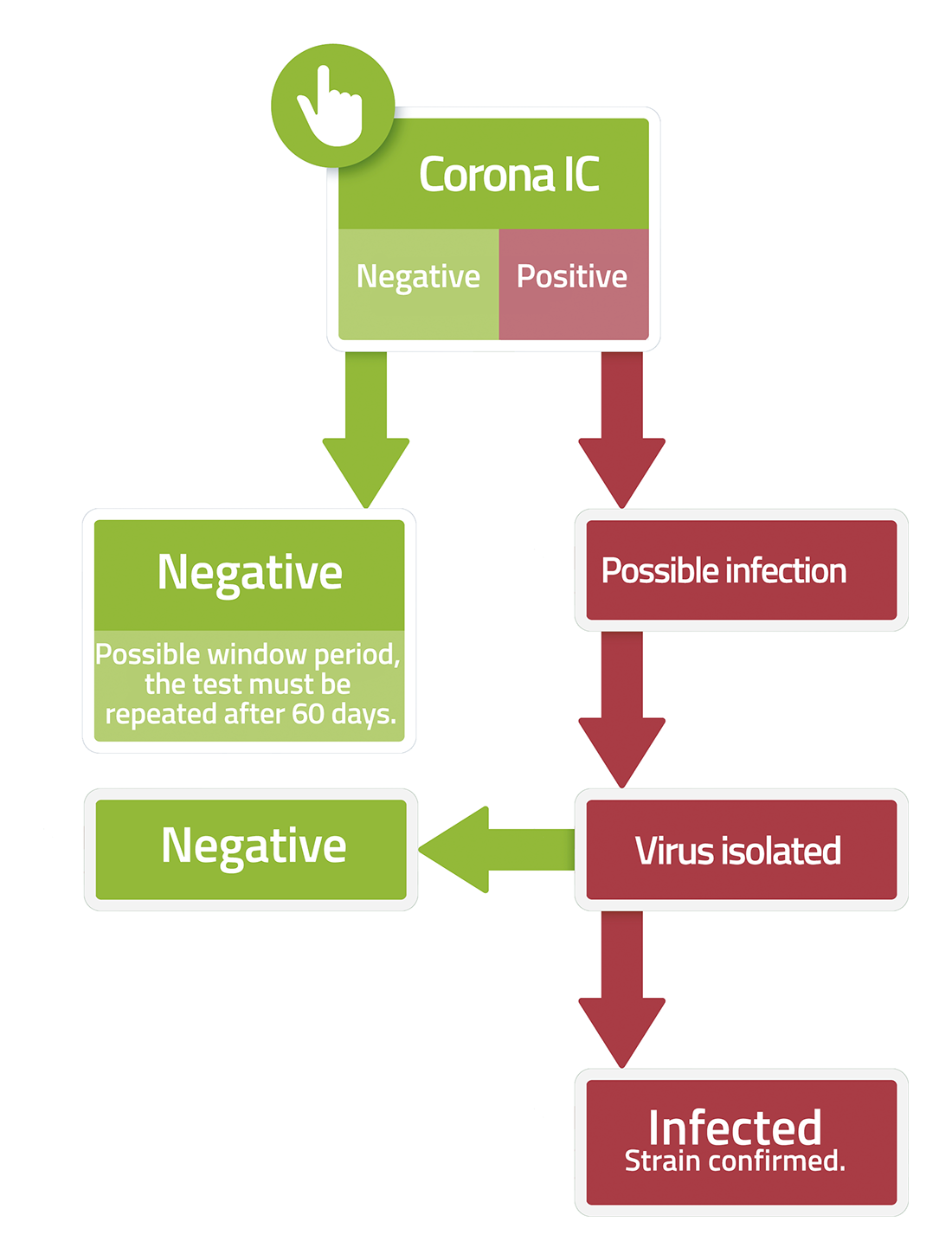
CORONAVIRUS
The incubation period is short, from 1 to 4 days.
After 3-4 months of infection CCoV can usually be present in the faeces of infected dogs.
After infection, the virus migrates to the mature epithelial cells of the small intestine villi, in which attacks and damages them, and where it reproduces rapidly.
During infection, the virus and its viral antigens are then transported to the underlying lymphoid tissue. Absorption into intestinal lymphoid tissue suggests that CCoV may persist and become latent in some dogs.
CO-INFECTIONS
Dogs can become infected with both CCoV and CPV at the same time.
Many authors have observed that the severity of the infection tends to increase with co-infection.
It has also been observed that concomitant infection with canine adenovirus-1 and CCoV may increase the severity of the infection.
Likewise, infections combined with canine distemper have greater severity and mortality.
PARVO
The course of parvo is variable from subject to subject even within the same litter. There are basically two clinical forms: one gastrointestinal (of variable severity) and one cardiac; however, a sub-clinical form is also recognized.
Gastrointestinal form:
After a short incubation period, the following appears:
- vomiting and diarrhoea with blood
- anorexia
- depression of the sensory
- dehydration rapidly sets in and, sometimes, even mild hyperthermia
- leukopenia (<3000 cells / mm3) with marked lymphopenia.
.
The course is variable and a slow recovery or a worsening of the general conditions with death of the affected subjects can be observed.
Heart shape:
Clinical evolution is rapid and 2-4 weeks old subjects die with the signs of acute myocarditis.
Subclinical form:
It is perhaps the relatively most frequent form, characterized by:
- mild sensory depression
- anorexia
- mild diarrhea
- modest leukopenia / lymphopenia.
.
The development of the sub-clinical form, sometimes asymptomatic, is closely correlated with the degree of immunity of the animal at the time of infection. Obviously, this is a partial immunity that does not prevent the replication and excretion of the virus. This clinical form takes on a different epidemiological importance depending on the type of life of the animal. In a puppy living in a family environment, the infection will have a limited epidemiological impact; on the contrary, the same situation projected inside a breeding / kennel takes on a completely different implication, as the infected animal eliminates the virus with the faeces and can transmit the infection to other subjects.
CORONAVIRUS
Coronavirus infection is usually less dramatic than parvo infection. Clinical signs can vary greatly in dogs of any breed, age and sex. The main clinical signs are:
- Nausea,
- Vomiting,
- Diarrhea.
- Orange colored stools, very bad smelling
- Presence (rare) of blood in the stool
- Loss of appetite
- Lethargy
.
The clinical signs may be more serious, depending on whether the infection is sustained by particularly virulent strains or in very young puppies.
Symptoms are not very specific, so it is of fundamental importance to carry out a test.
Coronavirosis mainly affects the cells of the digestive system damaging them.