FLUO DISTEMPER
IFA kit for the detection of anti-Canine Distemper Virus IgG antibodies
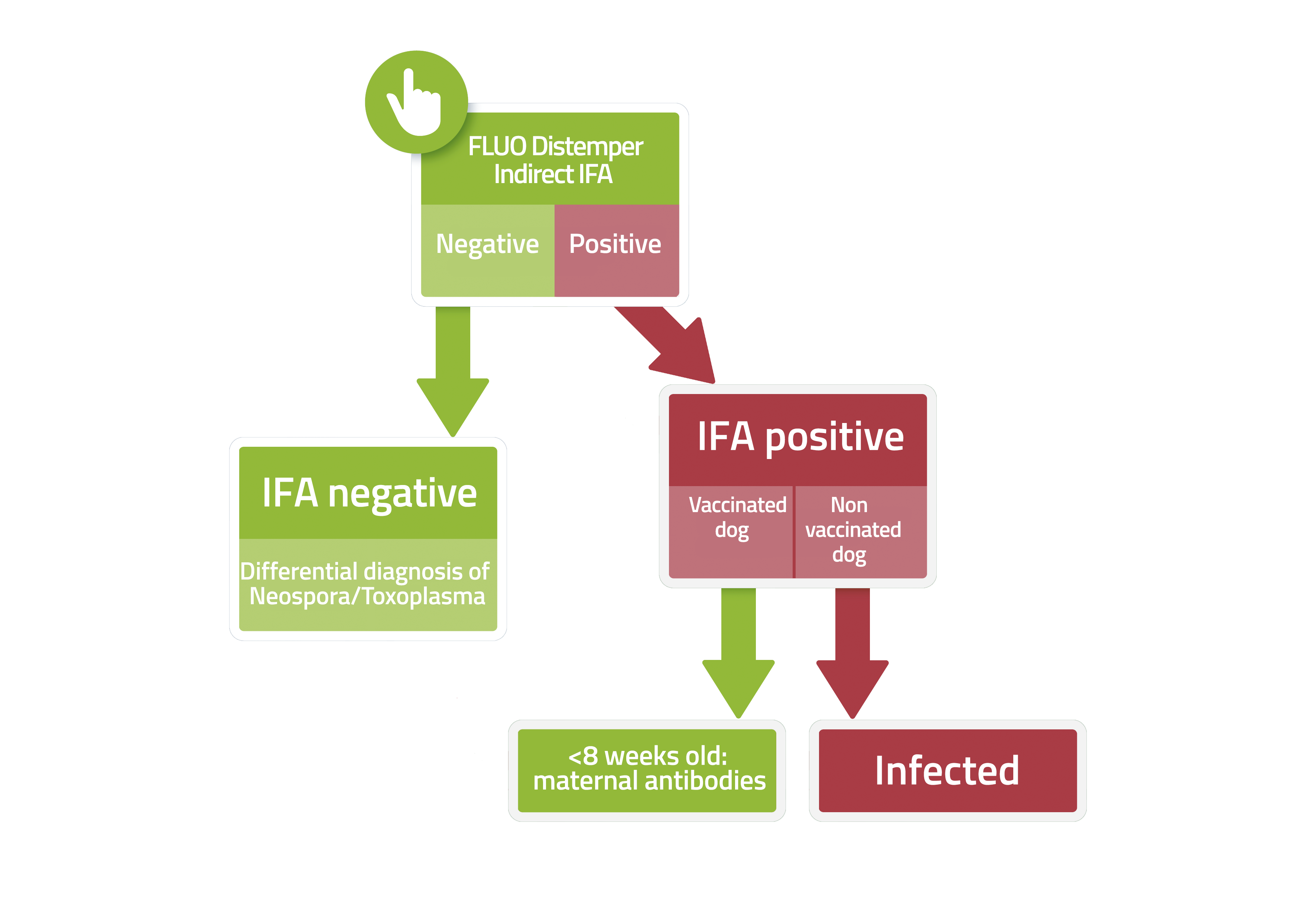
Fluo DISTEMPER is a test based on the immunofluorescence technique for the detection of anti-Canine Distemper Virus (CDV) IgG antibodies in dog serum or plasma samples.
Distemper is a systemic disease that affects dogs and other wild canids.
The aetiological agent is a morbillivirus (Canine Distemper Virus – CDV) of the family Paramixoviridae.
The virus particularly affects puppies, regardless of breed. It is present all over the world and is particularly wideasperad in the cities, dog colonies and in general wherever dogs are in contact with each other.
Although the virus is contagious, it shows a poor environmental resistance bacause it is sensitive to UV rays, heat, desiccation and is rapidly inactivated by common disinfectants.
The virus is transmitted by direct contact, inhalation and trans-placental route. The virus is excreted in the faeces and secretions in the acute phase of the infection and localizes in the nervous system, eyes, skin and lungs. Symptoms are variable and can affect the respiratory, digestive and nervous system.
Mortality can reach 50%, especially in young and unvaccinated animals.
Distemper is an insidious disease: the symptoms that distinguish it, taken individually, lead back to simple, common and not very serious pathologies. The first symptom usually is fever.
The virus induces serious respiratory, gastrointestinal, dermatological and neurological problems at a more advanced stage of the disease.
- Respiratory problems: nasal discharge, cough, breathing difficulties
- Problems with the digestive system: gastroenteritis with vomiting and diarrhea.
- Skin problems: dermatitis, thickening of the skin of the nose and pads.
- Nervous system problems: convulsions, muscle spasms up to paralysis of the limbs.
- Eye problems: conjunctivitis with ocular discharge.
Following a transient leukopenia induced by viral infection, the secondary bacterial infection usually shows up with a leukocytosis. The transient drop in white blood cells further weakens the immune system as a result of the sick puppy being exposed to secondary infections that complicate the clinical picture.