Giardia IC
Rapid Test for the determination of the Giardia lamblia antigen
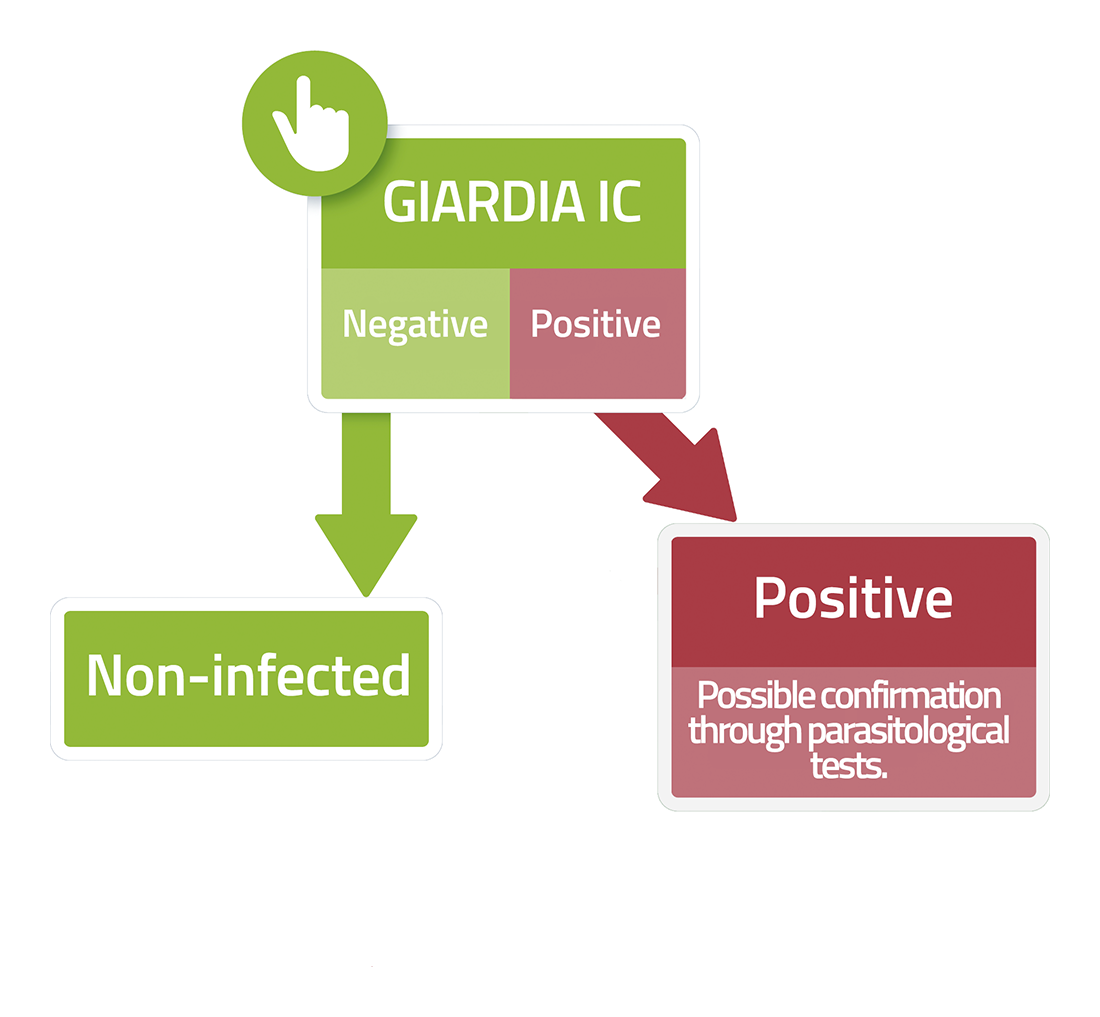
Giardia IC is an immunochromatographic test for the detection of the Giardia lamblia antigen in canine and feline faeces samples.
Giardiasis is caused by Giardia, a unicellular parasite belonging to the flagellated protozoa (Giardia intestinalis, or duodenalis or lamblia). It can affect dogs, cats, other animals and even humans indifferently, causing a disease also known as giardiasis (in human part of the traveler's diarrhea complex).
Normally the transmission of Giardia occurs via the oral-fecal route through the ingestion of contaminated food, water or soil. The life cycle is direct and does not require intermediate hosts.
Giardia in faeces occurs in two forms: the mobile, flagellated (i.e. the form taken in the intestine) or cystic (most common to be found in faeces tests). In the cystic form, giardia is able to survive for several months in the environment, especially where there is a lot of water and humidity. Once the cysts enter the organism orally, they mature in the intestine and become trophozoites. Here they reproduce and can begin to produce cysts that are excreted through the faeces.
The spread of Giardia is about 10% in dogs living in the family, from 36 to 50% in puppies and up to 100% in breedings.
The prevalence in cats ranges from 1.4 to 11%.
Most infections in which cysts pass in the faeces are asymptomatic. However, sometimes the symptoms can become manifest, especially in puppies and kittens, in elderly animals, in debilitated animals, in those suffering from other diseases (for example cats with FIV and FeLV), in those with multiple intestinal worms.
The main symptoms are:
- diarrhea (acute, liquid, manifesting as a single very strong discharge or with multiple and repeated discharges)
- weight loss
- mucous and foul-smelling stools, sometimes with blood streaks
- sometimes lethargy in cats
- decreased appetite
- stunted growth.